
(" (%s daylight saving time will be in effect. If (arrivingZone.getRules().isDaylightSavings(arrival.toInstant())) This page will be updated when a change in observed UTC offset occurs, such as when DST begins or ends somewhere. ("ARRIVING: %s (%s)%n", out2, arrivingZone) Regions with multiple time zones have a dashed underline. World Clock Current local time around the world. ZonedDateTime arrival = departure.withZoneSameInstant(arrivingZone) Time Converter Compare cities or time zones across the world.

ZoneId arrivingZone = ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo") Flight is 10 hours and 50 minutes, or 650 minutes ("LEAVING: %s (%s)%n", out1, leavingZone) ZonedDateTime departure = ZonedDateTime.of(leaving, leavingZone) Even though the Pacific time zone is only used in individual regions of three countries, it is known worldwide due to the large metropolitan areas on the. ZoneId leavingZone = ZoneId.of("America/Los_Angeles") LocalDateTime leaving = LocalDateTime.of(2013, Month.JULY, 20, 19, 30) Leaving from San Francisco on July 20, 2013, at 7:30 p.m. The ZoneRules.isDaylightSavings method determines whether it is daylight saving time when the flight arrives in Tokyo.Ī DateTimeFormatter object is used to format the ZonedDateTime instances for printing:ĭateTimeFormatter format = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("MMM d yyyy hh:mm a") The withZoneSameInstant and plusMinutes methods are used to create an instance of ZonedDateTime that represents the projected arrival time in Tokyo, after the 650 minute flight.
#City time zone list full
It is used to represent a full date (year, month, day) and time (hour, minute, second, nanosecond) with a time zone (region/city, such as Europe/Paris).įlight example, defines the departure time for a flight from San Francisco to Tokyo as a ZonedDateTime in the America/Los Angeles time zone. ZonedDateTime class, in effect, combines the The ZonedDateTime class accommodates this scenario, whereas the OffsetDateTime and OffsetTime classes, which do not have access to the ZoneRules, do not. For example, most time zones experience a gap (typically of 1 hour) when moving the clock forward to daylight saving time, and a time overlap when moving the clock back to standard time and the last hour before the transition is repeated. ZoneRules, part of the package, to determine how an offset varies for a particular time zone. Also, XML and other network formats define date-time transfer as OffsetDateTime or OffsetTime.Īlthough all three classes maintain an offset from Greenwich/UTC time, only ZonedDateTime uses the
#City time zone list software
When would you use OffsetDateTime instead of ZonedDateTime? If you are writing complex software that models its own rules for date and time calculations based on geographic locations, or if you are storing time-stamps in a database that track only absolute offsets from Greenwich/UTC time, then you might want to use OffsetDateTime. OffsetTime handles time with a corresponding time zone offset from Greenwich/UTC, without a time zone ID.OffsetDateTime handles a date and time with a corresponding time zone offset from Greenwich/UTC, without a time zone ID.ZonedDateTime handles a date and time with a corresponding time zone with a time zone offset from Greenwich/UTC.The Date-Time API provides three temporal-based classes that work with time zones: This is used for recurring times (such as in a Calendar program) that change between summer and winter.The TimeZoneId example also prints a list of all time zone IDs to a file called

Summer (daylight) time, such as "Atlantic Daylight Time" In Haystack, we use the term timezone to encapsulate two concepts: offset from UTC. Winter (standard) time, such as "Atlantic Standard Time" Timezones are identified using the tz tag with a city name from the. For example, the English America_Mountain "Mountain time" can be ambiguous and including "Rocky" may be most commonly understood in your language thus the translation would be for "Rocky Mountain time".įor each of the first two, there are three choices: Time in the United States The United States is divided into 6 time zones. When the English name can be ambiguous in your language, use the name that's most commonly used. For example, “Central time” would be ambiguous without the America_Central region context.
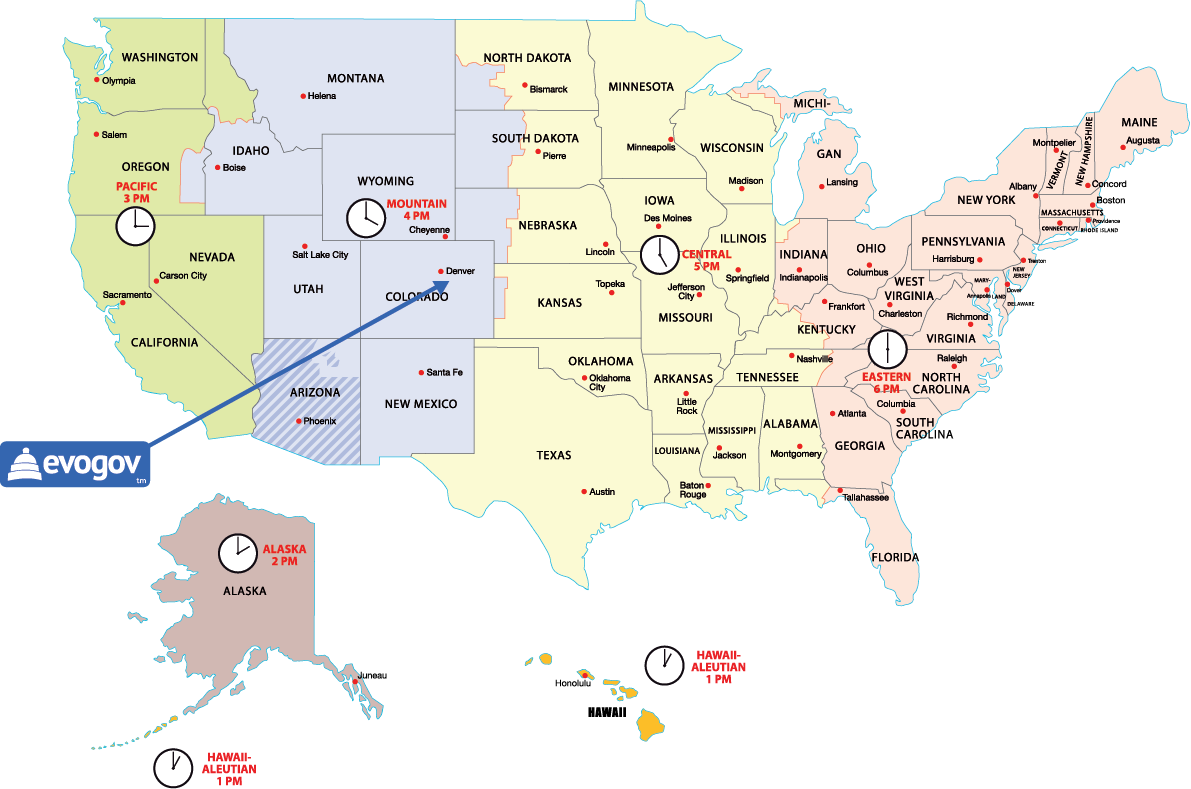
When translating time zone names, include the Region information if the name can be ambiguous. These are constructed using patterns (see below). When a "metazone" name is absent, a location based name is used as a fallback.
#City time zone list plus
These are constructed using patterns (see below), plus Country/Region Names and City Names. Location (country or city) based names, such as "Paris Time" or "Japan Standard Time"
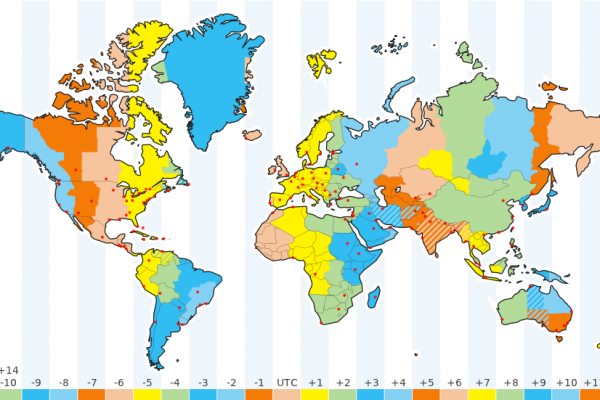
"metazone" names, such as "Pacific Time" or "Pacific Standard Time", that can apply to segments of a country or groups of countries. Time zones (such as "Pacific Time" or "France Time") can be formatted in different ways:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
